Prerequisites
Connection Methods
Choose the authentication method that fits your SQL Server configuration.
SQL Server Authentication
Use SQL Server username and password authentication.
Windows Authentication
Use Windows Authentication for integrated security.
Azure SQL Database
Connect to Azure SQL Database with connection strings.
Connection Guide
Step 1: Access SQL Server Integration
Navigate to Integrations in Datapad and select Microsoft SQL Server:
Step 2: Enter Connection Details
Fill in your SQL Server connection information:
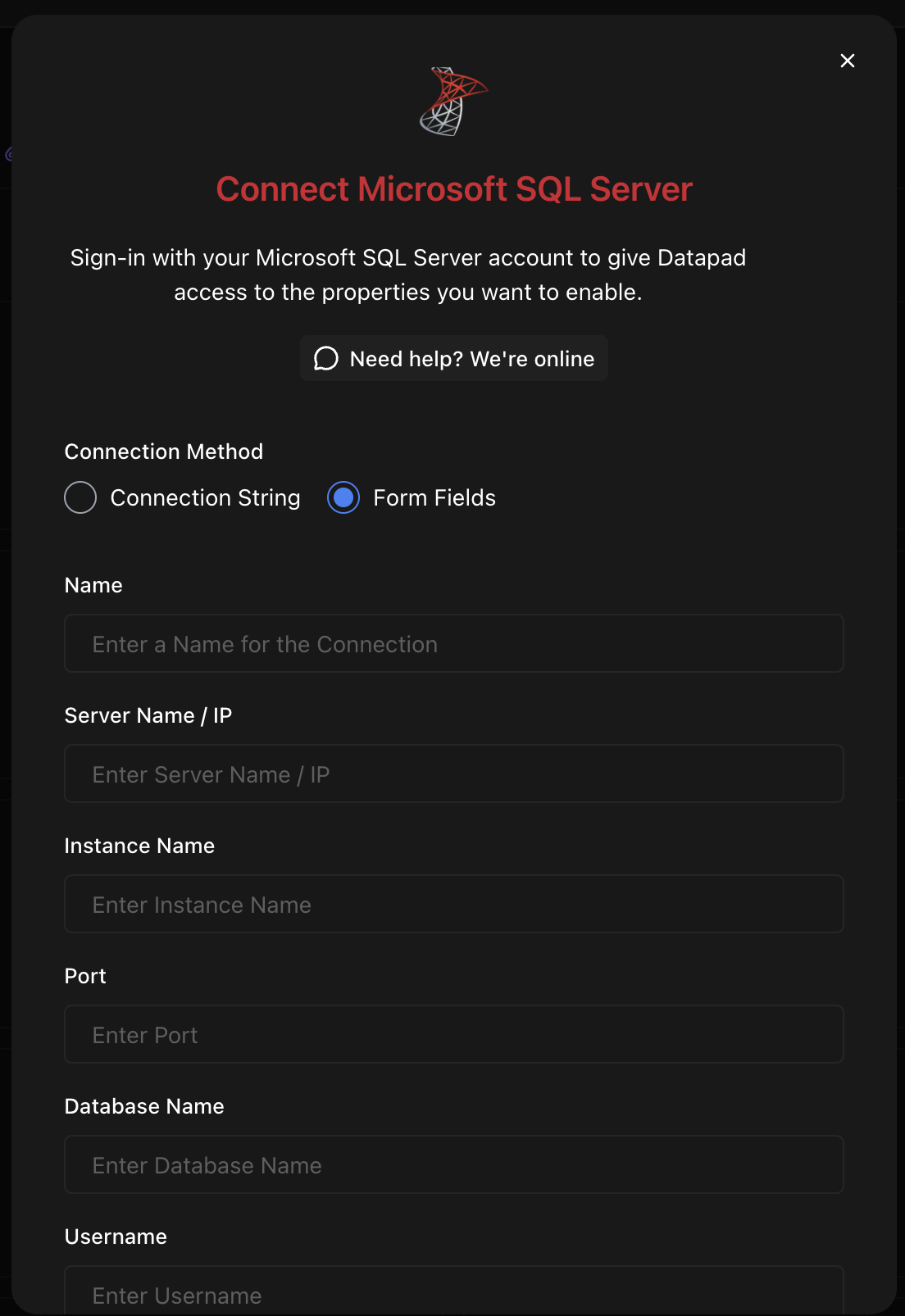
Required Fields:
- Server Name/Instance
- Port (default: 1433)
- Database Name
- Authentication Method
- Username and Password
- Encryption Settings
Step 3: Configure Security Settings
Select encryption and security options:

Security Options:
- SSL Encryption (recommended)
- Trust Server Certificate
- Connection Timeout
- Command Timeout
Create Read-Only Login (Recommended)
For security, create a dedicated login with read-only permissions:
-- Create a new login for Datapad
CREATE LOGIN datapad_readonly WITH PASSWORD = 'SecurePassword123!';
-- Create user in your database
USE your_database;
CREATE USER datapad_readonly FOR LOGIN datapad_readonly;
-- Grant read permissions
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER datapad_readonly;
-- Grant view definition for metadata access
GRANT VIEW DEFINITION TO datapad_readonly;
Example Queries
Here are some example questions you can ask once your SQL Server data is connected:
💬 Enterprise Query Tips
Behind the Scenes
Datapad connects to your SQL Server database using secure protocols and generates optimized T-SQL queries that leverage SQL Server-specific features like CTEs, window functions, and advanced analytics. Our AI understands SQL Server's unique syntax and performance characteristics to provide fast, efficient database analysis.
Troubleshooting
Connection failed
If SQL Server connection fails:
- Verify SQL Server is configured to accept remote connections
- Check that TCP/IP protocol is enabled in SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Ensure the SQL Server Browser service is running (for named instances)
- Test connectivity using SQL Server Management Studio
Authentication error
If authentication fails:
- Verify login credentials are correct and account is active
- Check if the login has access to the target database
- Ensure Windows Authentication is properly configured (if using)
- Try connecting with SQL Server Management Studio using same credentials
Firewall and network issues
If network connection fails:
- Verify SQL Server port (usually 1433) is open in firewall
- Check that SQL Server is listening on the correct IP address
- Ensure no network security groups are blocking connections
- Test network connectivity using telnet or similar tools
Permission errors
If you get permission-related errors:
- Verify the user has db_datareader role in the target database
- Check that VIEW DEFINITION permissions are granted for metadata access
- Ensure the user can access system views needed for schema analysis
- Contact your DBA if additional permissions are required