Have you ever wondered how stupid it would be if someone asked you to throw darts in the dark? 🎯
If you can visualize this situation, you know how a startup would be without tracking key performance indicators (KPIs).
Startups may have a lot to focus on, but if they don't do this one thing right, they will crash even before they take off.

Tracking KPIs for startups can get them to understand their target market, how customers like their product, and how to improve CX.
We know the importance of it, and that’s why in this article, we will tell you some of the crucial startup KPIs you need to track if you’re a startup founder and how to track them.
What are Startup KPIs? Why Do You Need to Track KPIs for Startups? What Are the 10 Most Important KPIs You Should Track? How do Startups Know What KPIs to Set and Track? How to Track Your Startup KPIs with Datapad?
What are Startup KPIs?
Businesses use metrics to measure their value and success. Most startups have only two things in mind when they kick things off - Revenue and Investment.
Being a part of a startup, it becomes even more necessary to know about the KPIs as these help keep you on a focused path essential to achieving sustained financial success down the road.
Startup KPIs are different from metrics that simply show the outcome of a particular activity. Instead, startup KPIs show you what every step of the customer journey looks like.
KPIs allow startups to identify, evaluate, and develop a better strategy to improve operational efficiency. Without that, no startup can drive meaningful growth.
Not only that, no startup has ever been successful without tracking KPIs. They’re the quantitative and qualitative measures that enable startups to grow and, more importantly, sustain growth.
That being said, let’s see why startup KPIs are important to track.
Why Do You Need to Track KPIs for Startups?
Tracking KPIs is crucial for startups as it allows them to evaluate their process and better understand their current efforts and related outcomes.
If you don’t consider tracking KPIs and key metrics, you might make random decisions based on nothing, and it can cost your company a fortune.
So, here are some reasons why tracking KPIs are important for startups:
#1. KPIs Show You the Right Path
By tracking certain KPIs, startups can get an insight into recent progress, which allows them to forecast their future growth.

Let’s consider a SaaS startup issue, for example.
The startup is dealing with a major issue with the company's revenue. They see a monthly decline in their revenue, and it’s breaking their team apart.
What do they do? 🤔
The CEO of this startup tracks the monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and customer churn rate and finds out that they’re having a hard time retaining customers.
When the CEO further analyzed the situation, he discovered that the software's UX was nowhere close to its competition.
He then started improving the UX, and in 3 months, they were successful in retaining customers.
Therefore, tracking KPIs can show you where your product’s lacking and how to improve it.
#2. Highlights Gap
If you want to make it big, you must know where your product lacks. But just knowing isn’t enough. That’s why tracking KPIs help to recognize the areas of improvement in your current business model.
For example, if a startup comes to know it has a high burn rate, it can take steps in the right direction to cut off funding for secondary activities and reduce the burn rate over time.
#3. Helpful for Investors
Almost every startup needs funding to grow. And to impress your investors, you need to show the results. KPIs help you track results and show your investors the growth projections year-over-year.
Let’s say an investor asks you to present him your pitch.
They might want to look into revenue growth, cash burn, customer retention, and CAC. All these KPIs are important for them to know if the valuation you’re asking is fair or not.
Now that you know the importance of KPI tracking for startups let's look at the most essential KPIs you should track.
What Are the 10 Most Important KPIs You Should Track?
Here’s what a couple of experts said us when we asked them what they track for their startups and scaleups:Expert #1:
“We're still in the early stages at Contrast and in the Go-To-Market phase. We track the usual MRR, ARR, Churn rate and CAC by channel
At the beginning, we needed to be "demo-led" because the scope and value props in our product were evolving a lot. But as we are way more product-led now, we track a lot of value creation metrics like:
-
Livestream scheduled
-
Number of time you went in the studio
-
Livestream done
-
Number of clips made out of the raw recording”
Expert #2:
“We track KPIs like:
-
MRR: (Monthly Recurring Revenue) - does not include one-time, or nonrecurring revenue such as fees, etc.
-
ARR: (Annually Recurring Revenue) Measure of revenue components that are recurring in nature on an Annual Basis
-
Gross MRR Churn: Monthly recurring revenue lost in a given month / monthly recurring revenue at the beginning of the month
-
Paid CAC: Cost per Customer acquired through paid marketing channels (total sales and marketing spend in a given month / total customers acquired via paid channels, including via sales, in a given month)”
Here’s our expert opinion on what KPIs a startup should actually track.
#1. Total Addressable Market (TAM)
Total addressable market measures the target market a company is going for.
In other words, it gives an idea about the revenue a company can generate by selling its product and services.
But why does it matter so much? Why do companies rely on that?
Short answer - It gives you a roadmap for the future.
Let us explain how:
Tracking the total addressable market helps you determine the marketing needs of your potential customers. That can save you both time and other resources like money and human resources in carving out a perfect plan to execute your business.
Turns out that you can make a better business plan and budget estimate by tracking and understanding TAM better than your competitors.
In addition, it lets you assess how strong the market for your business is so that you could focus on the product evolution and revenue growth eventually.
This brings us to another question, how do you calculate TAM?
You can calculate TAM in three steps:
-
Top-Down: Estimates TAM using industry reports and data studies
-
Bottom-Up: Track projections based on your earlier sales
-
Value Theory: Understand how much your product is worth to your ideal customer
#2. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
Recurring revenue is the life force of SaaS businesses. It’s the income expected by the number of active subscribers month-over-month.
In subscription-based businesses, it’s quite normal for customers to buy, pause, and cancel subscriptions regularly.
However, if it remains untracked, the company fails to gauge its implications on the profit and overall revenue. That’s why monthly recurring revenue becomes essential for a business to measure the existing customer base.
Monthly recurring revenue is one of the most important metrics for SaaS companies.
Customers are the first and last indicators of a company’s success. And monthly recurring revenue paints a full picture of the customers who are joining and leaving your company (conversion rate).
By looking at MRR trends, you can know where your business is going and what you need to improve.
Moreover, it also helps to make accurate financial forecasting to decide what changes you need to make for increased monthly revenue.
Now that you know about the importance of MRR, you can calculate it by:MRR = Number of subscribers in the monthly plan X ARPU
Where,
ARPU is the average rate per user.
#3. Customer Churn Rate (CCR)
Do you know how many customers are leaving you monthly or quarterly?
If you don’t, then you are unaware of its impact on the overall revenue and your business.
Most importantly, if you don’t address this without being too late, you won’t be able to fill those gaps and save your startup from hitting the bottom of the ocean.
Scary, right? 👻
Customer churn rate, aka customer attrition rate, is the percentage of customers leaving your business in a given time period.
It can be a tough realization for any business but a useful indicator of how your business is working out. The higher the churn rate, the more customers go out.
Customer churn rate can be an intimidating KPI to track, but it’s also a crucial one that lets you understand your customer better. By tracking it right, you can analyze the gap between your deliverability and customer expectations.
And then, you can find a way to narrow that gap by improving your product over time.
However, this KPI doesn’t answer why people are leaving, and that makes it difficult to make a more specific approach to solve the problem.
Yet, it’s always good to know the reason behind the attrition, which you can calculate by:CCR = (Customer in the beginning - Customers in the end) / Customers in the beginning
#4. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
An advertisement means nothing to a customer if it’s not engaging enough. Today, many startups online use highly targeted campaigns to approach customers and convert them into potential buyers.
Customer Acquisition Cost is a crucial business metric that refers to the overall cost spent by a company on the potential customer to buy something. The cost includes everything like
-
Marketing efforts
-
Inventory
-
Production costs
And much more…
The importance of CAC has risen, particularly in internet-based companies, to make educated business decisions. It’s how they figure out if their money brought value or not.
Additionally, it also takes a more pinpointed approach to growing your clientele. Traditional companies used a shotgun advertisement strategy that would appeal to a large segment of people.
On the contrary, by combining CAC with targeted campaigns, you not only bring in specific customers but also know how much you are spending on attracting them. This can channel a company's effort resulting in higher profitability.
You can calculate CAC by using this simple formula:CAC = Cumulative costs spent on acquiring new users / Number of customers acquired
Note: The lower the CAC, the higher the profit margins. Moreover, your investors would be keen to look at your CAC as it shows the amount you spend to acquire customers.
#5. Average Revenue Per User
When it comes to startup KPIs, ARPU is an underdog. But that doesn’t make it any less important.
It refers to the revenue generated from every active subscriber. It’s an indicator of how profitable a company is because it tells how much the average user spends per subscription.
As compared to MRR, it’s a more straightforward KPI to measure the net growth of a company.
ARPU can be useful in numerous ways.
For starters, it helps you analyze the pattern to distinguish between the best and worst performing products.
Further, it lets the company decide where it wants to spend more for maximum growth. This way, ARPU helps the company in making the right decision that has a direct impact on its scalability.
The formula for calculating the ARPU is:ARPU = Total revenue during a specific time / Active users during that time
ARPU helps you understand your potential buyers clearly, which results in better price models.
#6. Monthly Active Users (MAU)
How would you know if your product is good or not?
It’s simple; if people are using it repeatedly, then it’s worth some value.
Similarly, monthly active users refer to the number of users who have engaged with your product in some way during the last 30 days. It’s a commonly used metric in social media to measure the success of a campaign.
MAU provides an overview of general business health.
Tracking MAU has proven to be one of the key things for startup owners.
That’s because the number of active users indicates that the customers are interacting with your products which is a healthy sign and suggests you are on the right path.
Moreover, MAU trends tell you about the perceived value of your product so that you can make necessary changes if it’s working well.
Determining MAU over a period of time helps to evaluate the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. This guides you to create better strategies to drive more growth and an enriching customer experience.
That being said, the calculation of MAU is slightly vague. Everyone has a different approach to calculating it.
Generally speaking, you can calculate MAU based on internet data. You can head to the platform where you track your website traffic and get an approximate MAU.
Pro Tip: If you’re in your early days, start tracking daily active users first (DAU).
#7. Revenue Growth Rate
In simple terms, the revenue growth rate is the rate at which the revenue has increased or decreased per month. It’s one of the most critical KPIs that indicates how quickly your startup is growing.
For example, if your startup’s first-month revenue is $1000 and it increases to $5000 in the second month, then the growth rate will be 400%.
Revenue growth encompasses everything, including sales, marketing, operations, etc. Thus it provides a comprehensive view of a startup’s growth.
Most importantly, the revenue growth rate should not be confused with the earning growth, which is revenue minus the cost of production.
You can calculate the revenue growth by using this simple formula:
Revenue growth = (Current period revenue - Previous period revenue) / Previous period revenue
#8. Monthly Burn
As the term suggests, monthly burn refers to how fast a company is expected to burn all of its cash reserves before generating positive cash flows.
It’s a common metric in modern-day startups that estimates how long they will burn their capital before they make any income.
For example, if the burn rate of a company is $5000, it means it spends $5000 cash in a month.
Tracking this can be useful in two ways:
-
Better financial understanding leads to smart business decisions in the future
-
Knowing about the burn rate, startups can plan for further investment in advance
Broadly, there are two types of burn rates:
-
Gross: Total operating expense of a company
-
Net Burn rate: Amount earned and amount spend
Here’s how to calculate both:
Gross Burn Rate = (Monthly operating expense / Starting capital) X 100
Net Burn Rate = (Revenue - Operating Expense / Startup Capital) X 100
#9. Customer Lifetime value (LTV)
Customer lifetime value refers to how much a business can benefit from a person's relationship with its brand. Roughly, it indicates how customers interact with your business.
CLV is a measurement of the overall customer relationship with the company and not just on a purchase basis. Though it boils down to assigning a single value to your customer, it has major benefits.
Firstly, it helps to serve your ideal customer base. Customer lifetime value indicates the amount of money customers will spend on your business over time.
That enables startup co-founders to develop a strategy to target those customers who will bring them maximum revenue directly.
That also helps to minimize the CAC, as once you know about CLV, you know where to put your maximum efforts to increase retention rate and spend less on acquiring new ones.
It’s always easier to serve old customers than to add new ones.
CLV identifies the specific customers that contribute most to your business. This allows you to retain them so that they stay with you for a longer time and spend more during that life cycle. This results in increased revenue over time.
By now, we have understood the importance of CLV. Let’s now look at how to calculate it:CLV = Customer Value X Avg. customer lifespan
Where,
Customer value = Average purchase value X Average number of purchases
Note: CLV is an incredible metric that tells you where your loyal customers are so that you can maximize your outcome by focusing on them.
#10. Return on Investment (ROI)
Simply investing in your business is not enough. You need to find out what you’re getting out of it.
Return on investment means how much profit or loss you make on an investment. It can be defined as the net profit divided by the total investment costs.
ROI is a useful KPI when you have to judge your performance and come to a concrete solution.
It analyzes and determines the profitability of the investments. Calculating ROI is the best way to measure your financial gains and investment returns.
Moreover, it also highlights a business's weak spots, which pushes you to shape a stronger strategy to achieve higher efficiency.
ROI is simple to calculate, you can get that by:
ROI = (Net profit / Investment) X 100
You can rely on ROI data to evaluate and understand how a particular investment worked for your business. If a certain kind of investment brings desirable results, you can focus more on that and leave the rest.
How do Startups Know What KPIs to Set and Track?
“We do OKRs each quarter. Generally based on the area of the business we think needs the most attention or is least optimized in the funnel. I agree that it is important to stay focused and choose one or two parts of the funnel and dedicate the quarterly metrics and resources to that part.” - Natalie Marcotullio (Head of Growth and Operations at Navattic)
Knowing what KPIs to track for a startup is often tricky and a crucial part of the process. If you make the wrong decisions in the initial phase, you will waste a significant amount of time tracking KPIs that aren't worth it.
Here’s what Leah Tharin (Product lead at Smallpdf) said when we interviewed her:
“When your startup is in a non-monetized phase, track KPIs like the number of users, the target market, and the audience.
At the initial stage of your startup your goal might be to track the number of users you can onboard on your platform. But if you’re a B2B business, it might also be important to ensure that you have the right customers.
To know this, you can do a sub-segmentation of your audience. This means instead of just saying that you want to onboard 100,000 users till the end of the year, ensure that 30,000 of those should be small businesses (or a segment that you think is a must-have target market for your product).
Lastly, keep KPI tracking simple for startups and don’t go into much detail or spend most of your time tracking them because it's still early days.”
Here’s what Datapad’s co-founder John Ozuysal has to say about tracking KPIs for startups:
“If you’re in the early stage try to tackle one thing at a time and set your KPIs around that main metric. If you’re working on your marketing funnel, try to go after one part of the funnel in a quarter. Go after acquisition if that is your goal and track KPIs around this.”
How to Track Your Startup KPIs with Datapad?

Datapad is a mobile-first KPI tracking app (available for both Android and iOS) that lets you create KPI dashboards, bring your team onboard, and track your KPIs on the go.
Step 1: Setting Up Goal on Datapad
As a startup, you should start the KPI tracking process by defining your goals with every KPI you want to track.
You can do that easily with Datapad. Here’s a GIF to show you how it's done.

Do the above process for all the KPIs you want to track and keep track of the progress weekly, monthly, or quarterly, as per your needs.
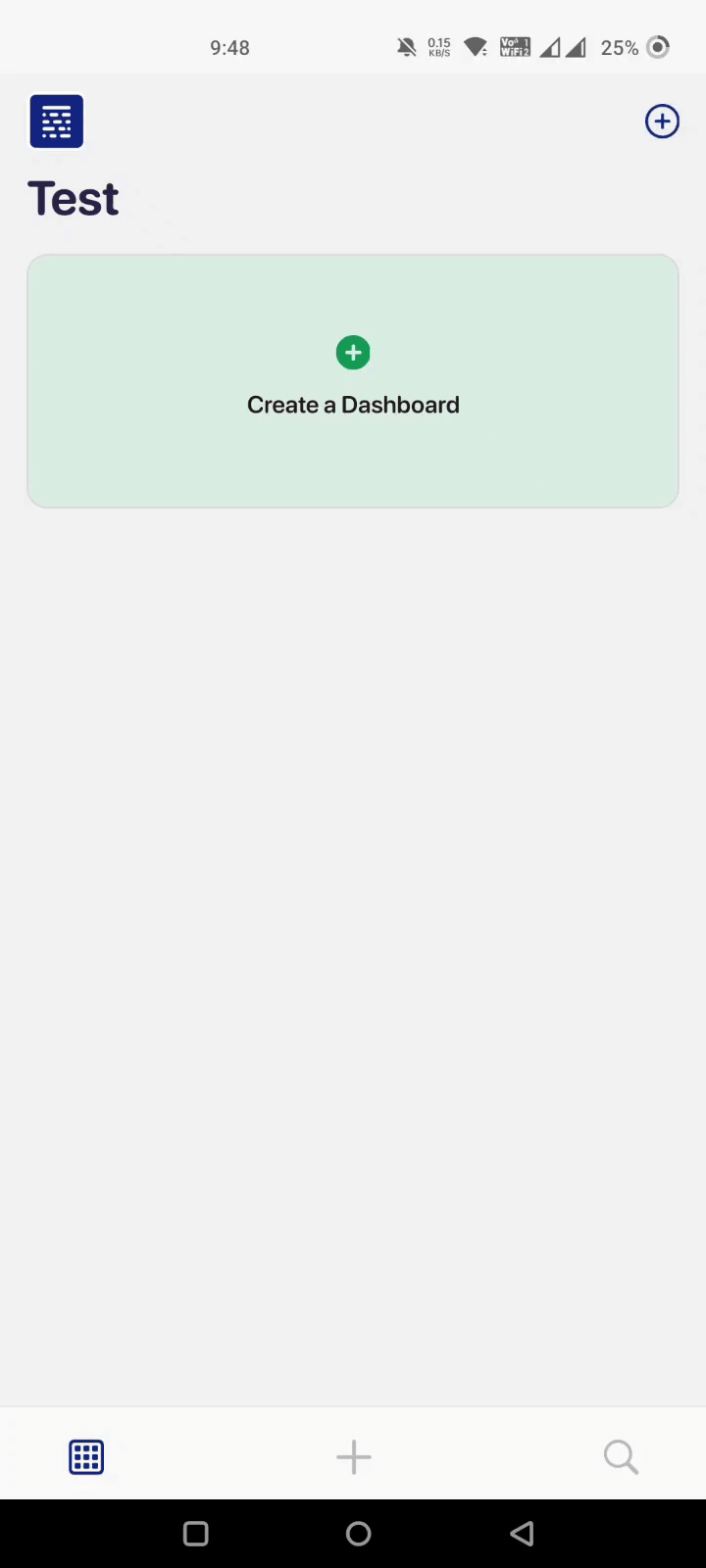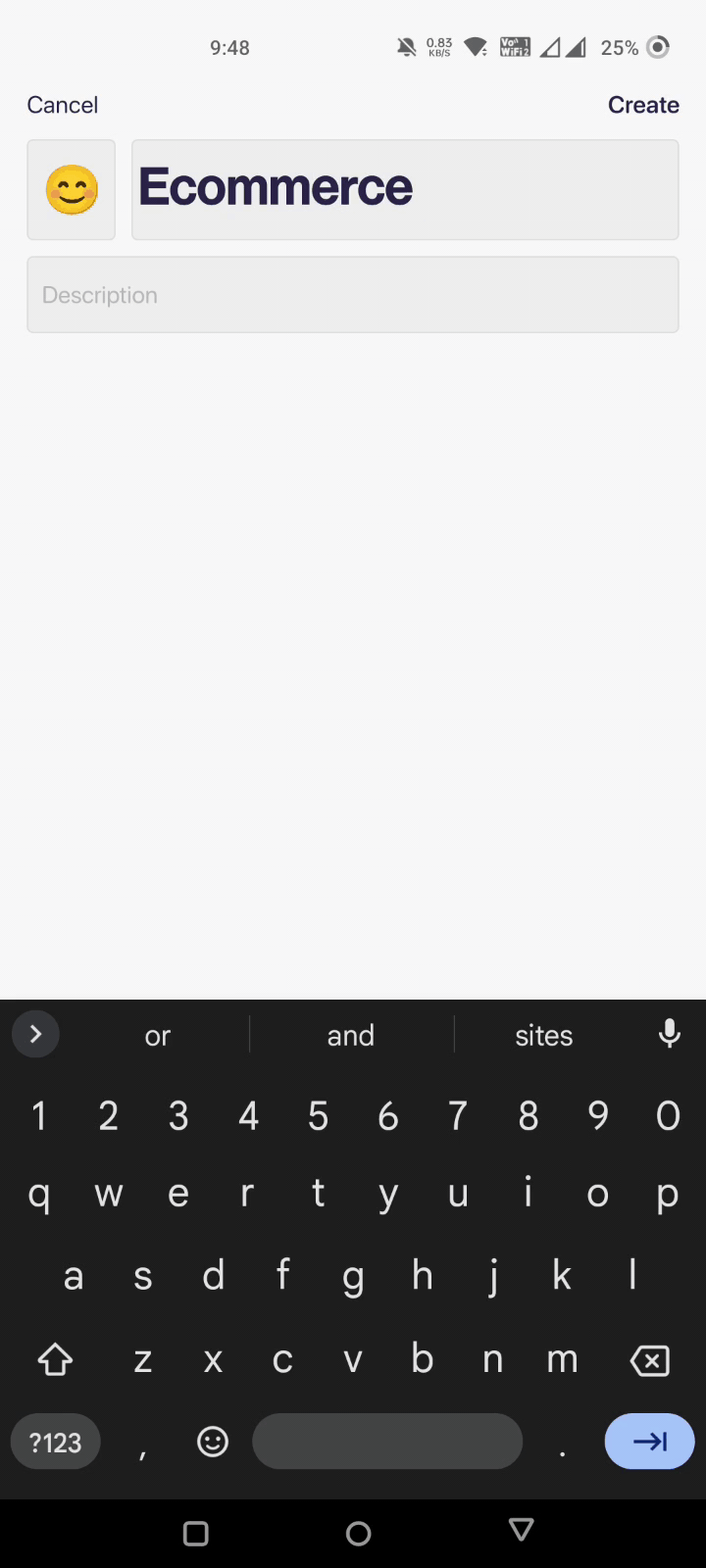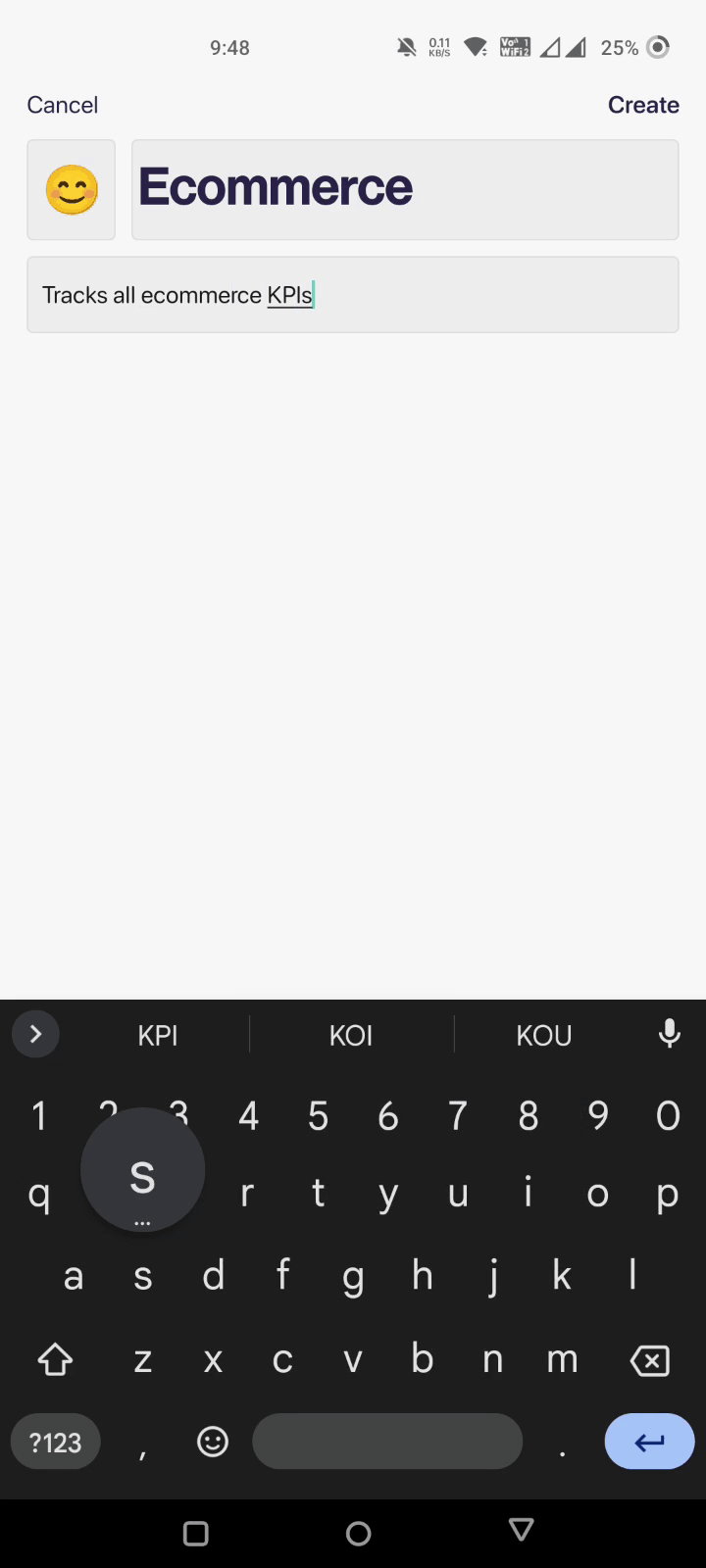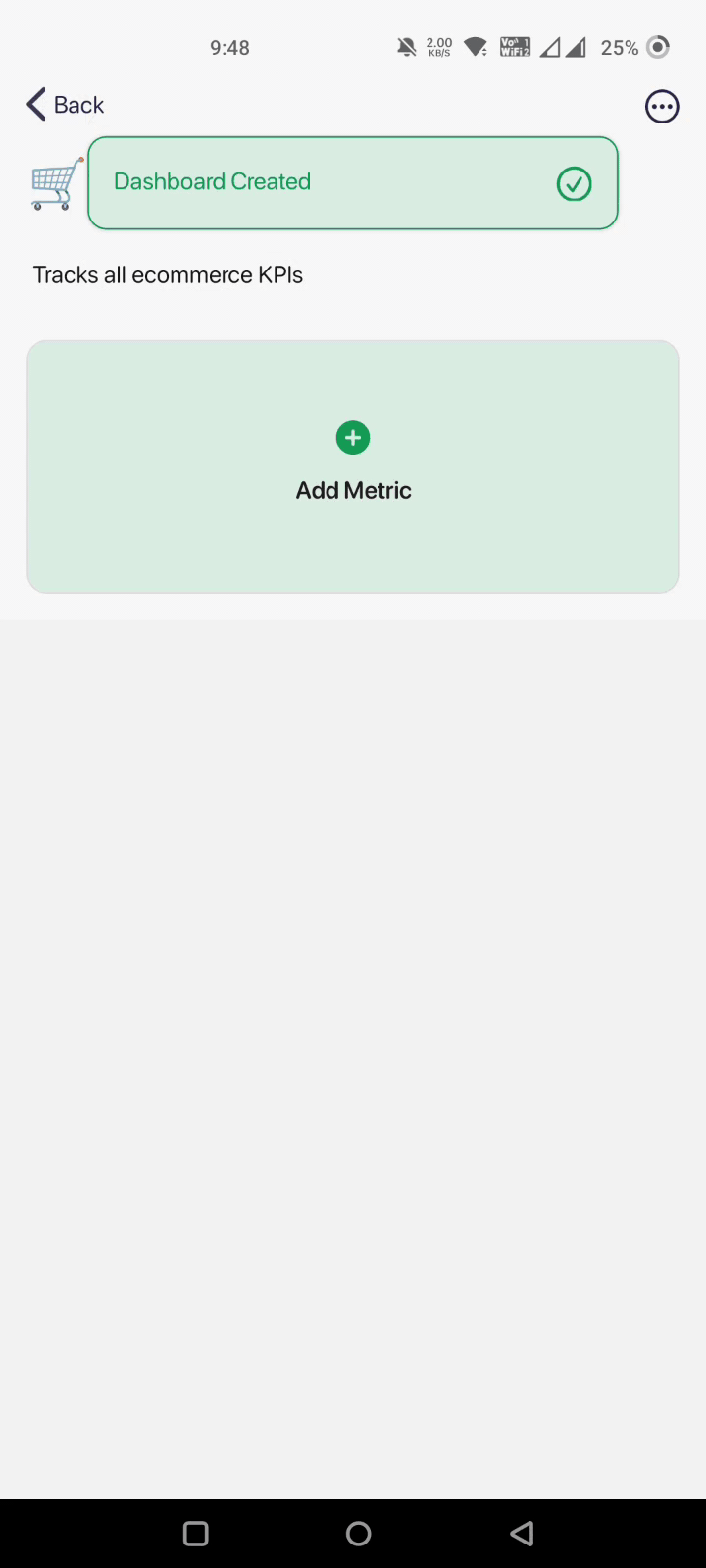
Step 2: Setting Up a Dashboard
Setting up a dashboard on Datapad takes just a few seconds. You can click on ‘Create a Dashboard,’ fill out the details for your KPI, add a touch of personalization, and click on ‘Create.’
That’s it; your brand new dashboard is on your phone screen.
Step 3: Import Data Automatically or Add KPIs Manually
To track any KPI, you need data around it. If you want to track website traffic progress, you need to know what your traffic was on day one and what’s the traffic now.
And to get this kind of data, you need to import it from the platform that helps you track it (in the case of the above example, it’s Google Analytics).
With Datapad, you can import data automatically with several one-click integrations we provide. Or you can even enter a KPI manually if you have less data that you’ve been tracking manually.
Along with importing data, you can also add KPI details, set goals, and customize the color according to your brand.
To import data automatically, the app has a button - Use a data source. Here’s how to use it:
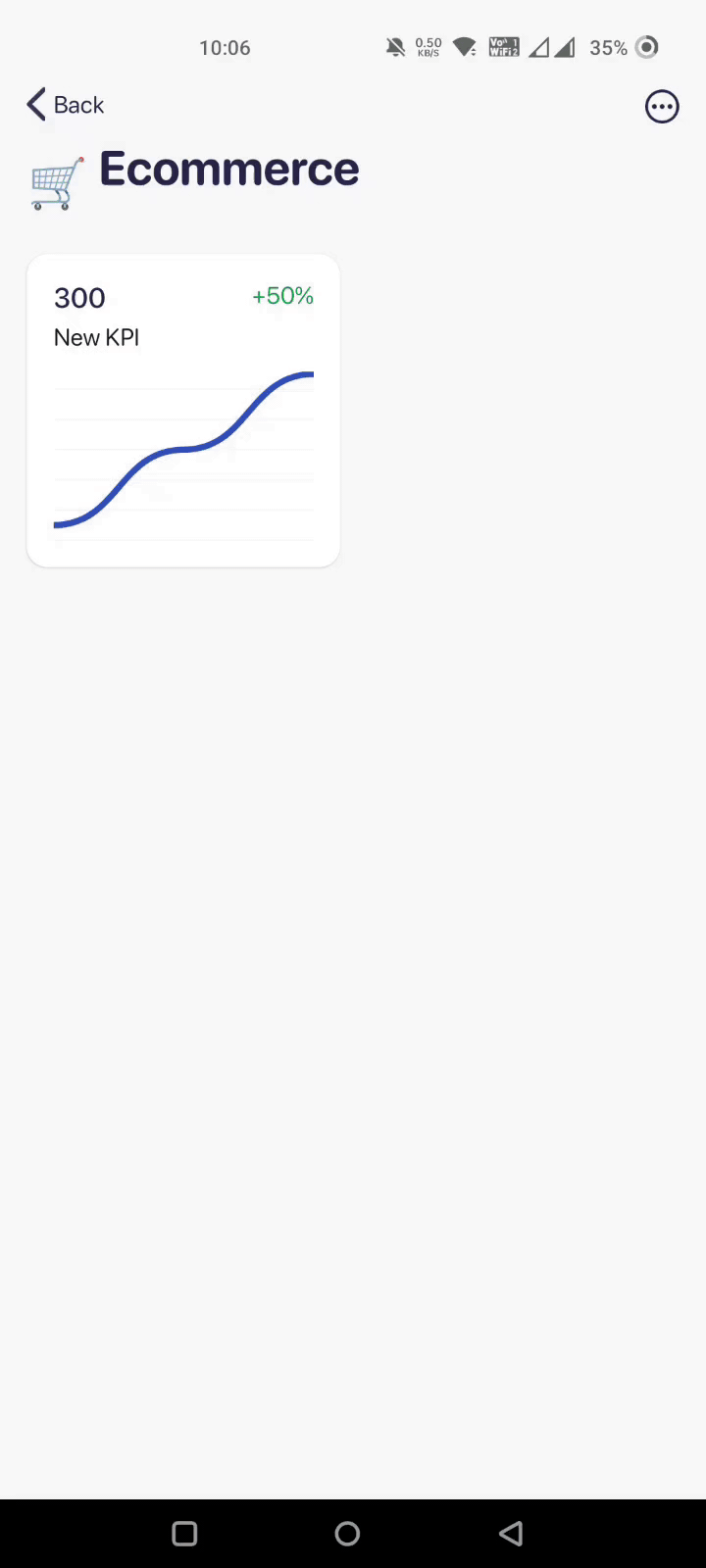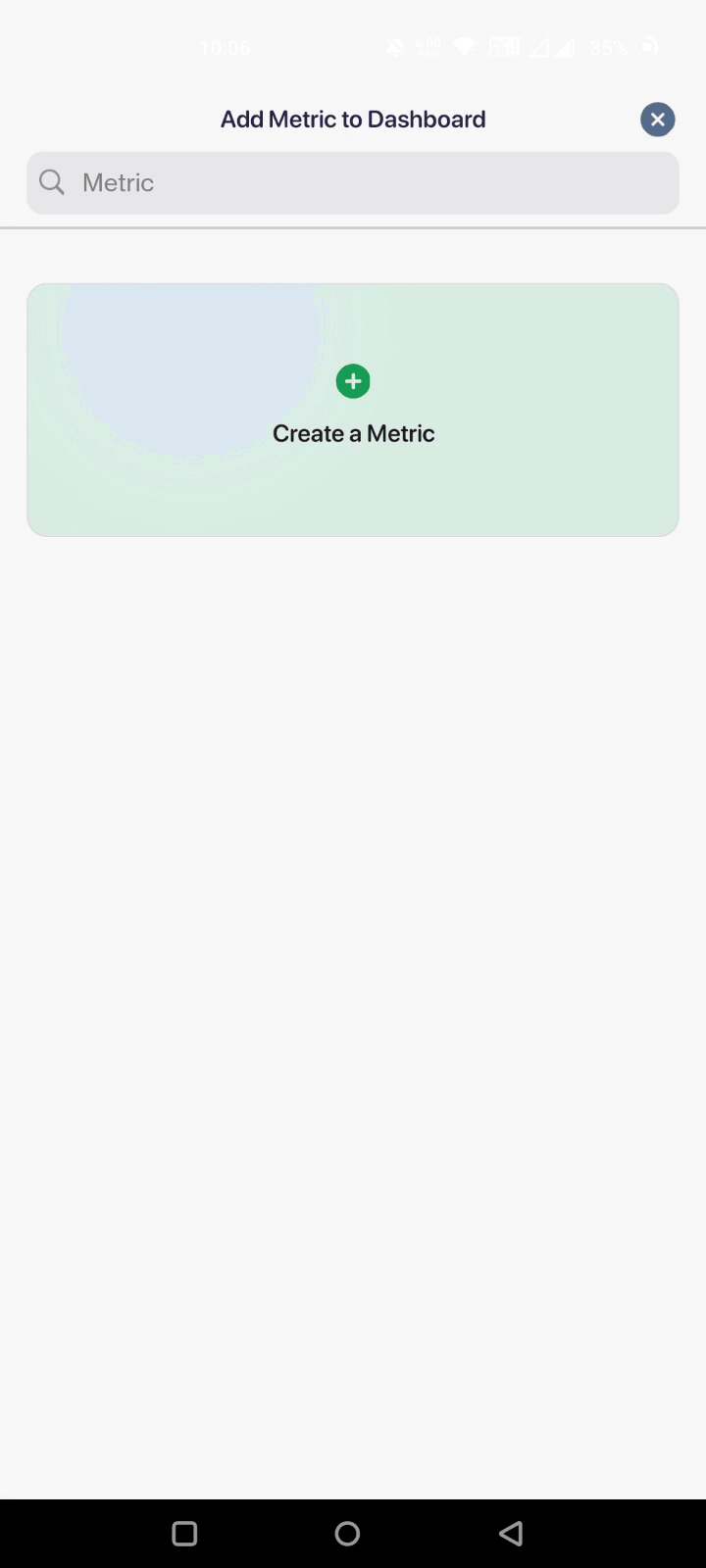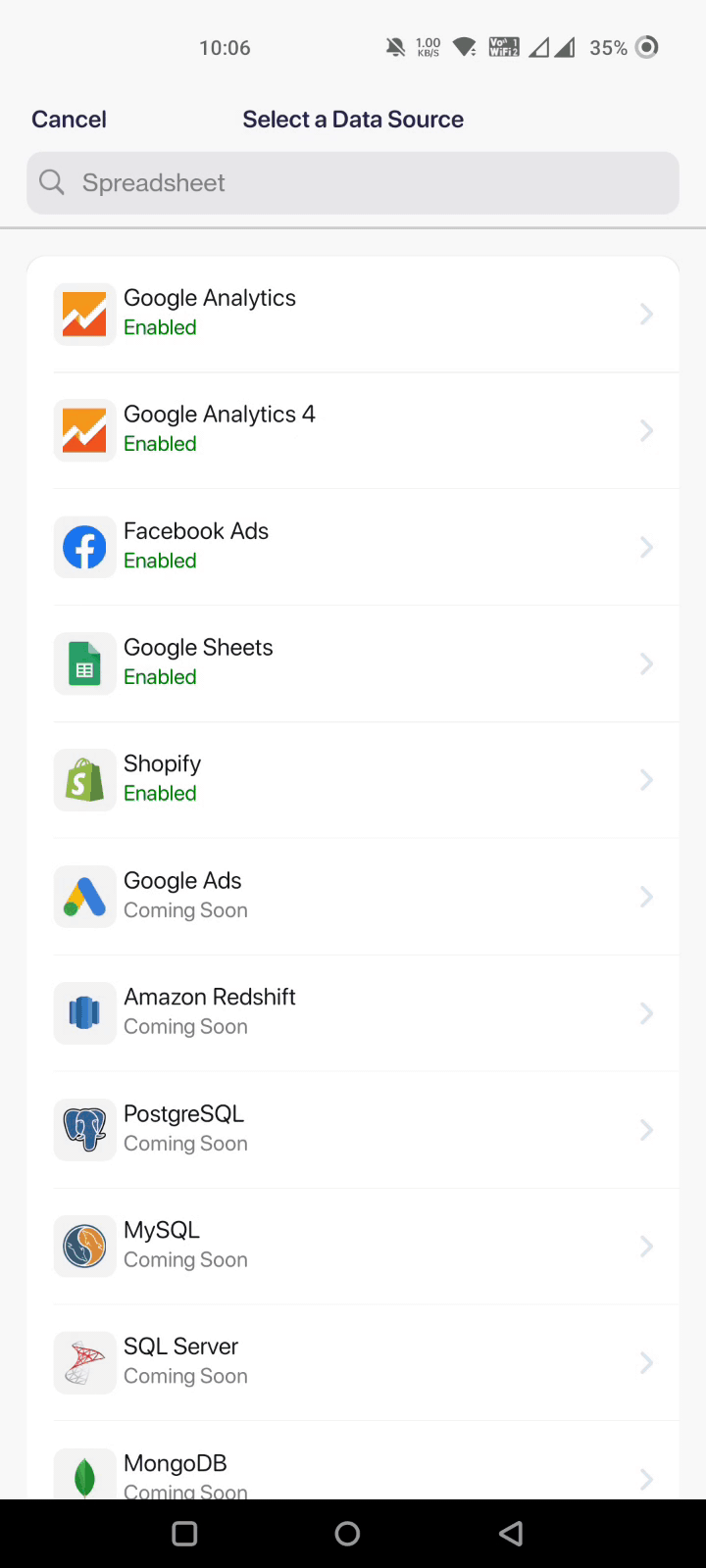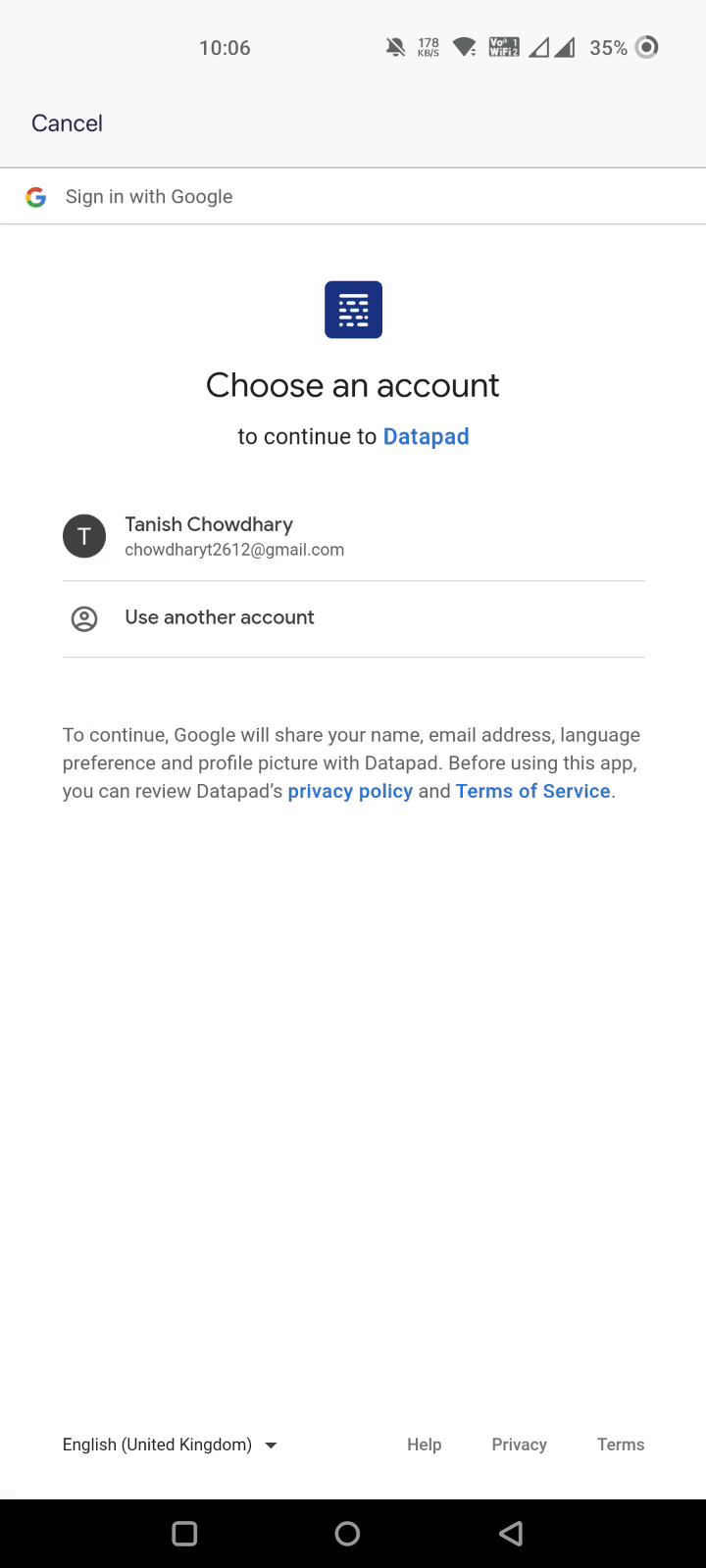
But if you’re planning to manually enter the KPI, you can just use our ‘Enter Manually’ option.
Step 4: Onboard Your Team
Onboarding your team to track KPI should be your first step as a startup. That’s because when every person in your team knows how the startup’s doing, they’d be able to think out of the box and suggest ideas that’d increase KPI performance.
Here’s how to onboard your team with Datapad:
-
Click on Datapad’s logo (top left-hand side of the screen)
-
Go to Manage users
-
Click on the ‘+’ sign on the top right-hand side corner
-
Enter the email address of your team member and tap invite users

Step 5: Monitor Your KPIs and Get Updated with Notifications
What good is tracking KPIs if you have no idea what’s going on, right?
Datapad gives you real-time and push notifications wherever a KPI underperforms or overperforms.
Not just this, every KPI you track has a comment section just below it that lets you chat with your team around the KPI wherever you want.
Datapad is a KPI tracking app that saves a boatload of time as you have all your KPIs in your pocket! 😀
All entrepreneurs can get started for free - no credit card required. Just sign up for free, download the app, and track KPIs from anywhere in the world. 🤗
Related:
-
13 Most Important SEO KPIs Every Business Owner Should Track in 2022
-
13 Email Marketing KPIs Every Marketing Professional Should Track
-
13 Software Development KPIs Every Dev Team Should Track
-
15 Best KPIs for Operations that Are a Must for Every Business to Track
-
15 Important Retail KPIs & Metrics to Track For Better Understanding of Your Business
![10 Startups KPIs You Need to Track [We Asked to the Experts]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fframerusercontent.com%2Fimages%2F3sX3rjmzlfZmeu9SoKe3QcaIfY.jpg&w=3840&q=75)